What is Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy is a method of performing surgery through small incisions. It is different from open surgery that we do with large incisions. Laparoscopic surgery is also known as "minimally invasive surgery".
Laparoscopy Treatment Types and Methods
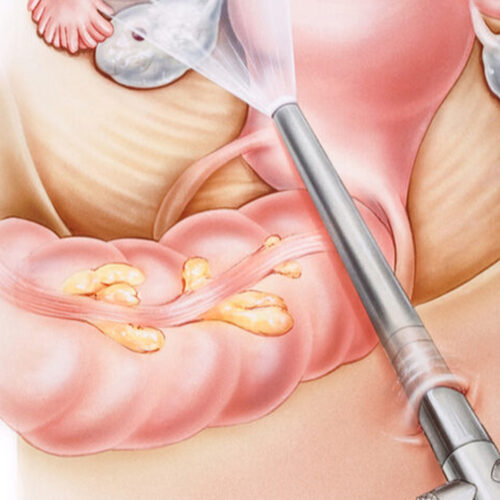
Uterine Prolapse with Closed Method
Detail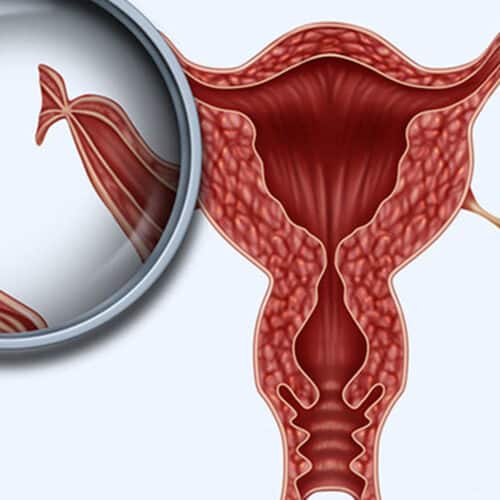
Tubal Reanastomosis
Detail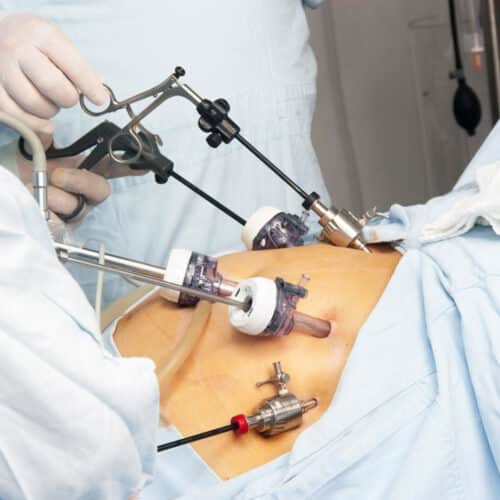
Sterilization by Laparoscopy
Detail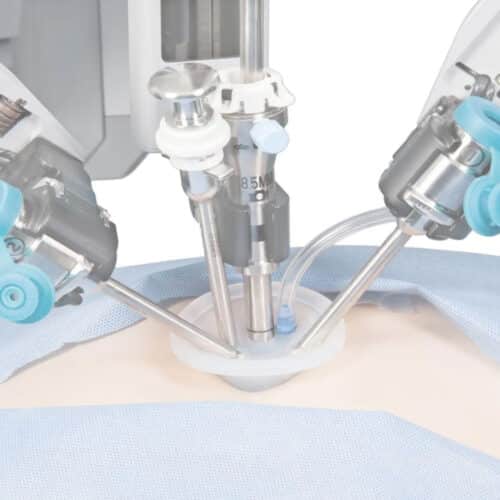
Robotic Uterine Removal Surgery
Detail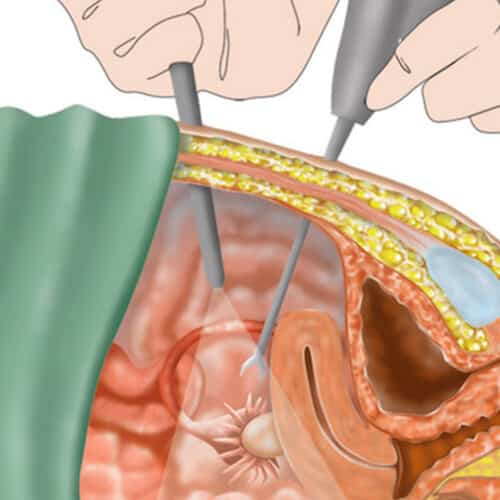
Removal of Tubes by the Closed Method
Detail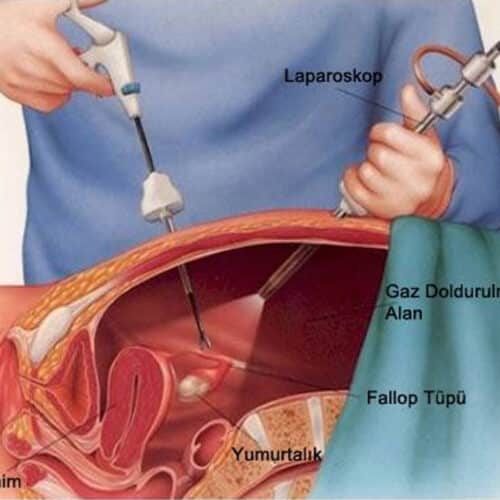
Laparoscopic Ovarian Surgery
Detail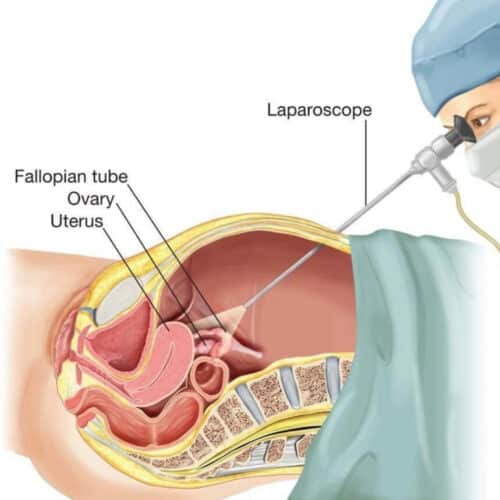
Laparoscopic Cystectomy
Detail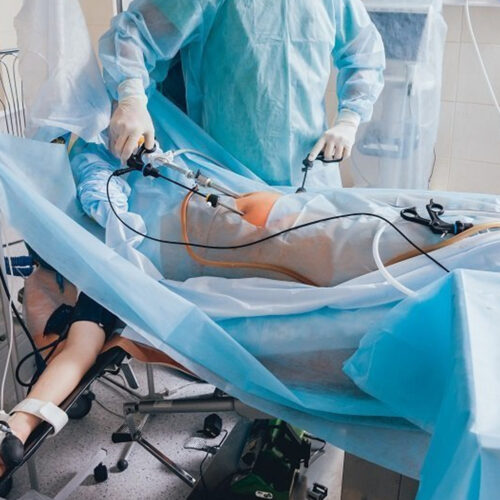
Closed Myoma Surgery
Detail
Closed Method Uterine Removal Surgery
Detail
Chocolate Cyst Surgery with Closed Method
DetailHow is laparoscopic surgery performed?
These operations are performed with a special instrument, the laparoscope. The laparoscope is a long, thin device that is inserted into the abdomen through a small hole. A camera is attached to the back, and through this camera, surgeons can examine the patient's abdomen and pelvic organs on an electronic screen. If there is a problem; They perform the operation with additional instruments. In these instruments, it is inserted into the abdomen through small holes. Sometimes all instruments are inserted into the abdomen through a single hole. These are called "single hole" laparoscopic surgeries.
What are the benefits of laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy has many benefits. It provides less pain, shorter hospital stay and faster recovery compared to open surgery. Patients who undergo laparoscopy usually recover quickly. Small incisions allow faster healing. In addition, the risk of infection is low due to small incisions.
What are the risks of laparoscopic surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery may take longer than open surgery. Prolonged stay under anesthesia increases the risk of complications. Sometimes complications do not appear immediately during the operation, but after a few days. The following complications may be encountered.
- Risk of bleeding or hernia at incision sites
- Internal bleeding
- Infection
- Injury of vessels or internal organs (stomach, intestine, ureter, bladder)
Which surgeries can be performed with laparoscopy?
- Tubal sterilization
- Ovarian cysts
- Chocolate cysts (endometriosis)
- Uterine removal
- Urinary incontinence
- Uterine prolapse
- Intra-abdominal infection, abscess
- ectopic pregnancy
- Myoma
- Cancer
- Infertility
- Chronic groin-abdominal pain
Is there any pain during the operation?
Laparoscopy is usually performed under general anesthesia. This is a form of anesthesia where you are completely asleep and feel nothing.
What happens during laparoscopy surgery?
After you get anesthesia and sleep, a 1-2 cm incision is made from the navel, the abdomen is entered and the abdomen is inflated by giving gas. The camera is then placed on your abdomen. By means of this camera, your organs are easily examined and observed.
